Unlocking Insights into the Supplement Consumer: Trends and Opportunities
Executive Summary
For more than two decades, MarketPlace has lived at the intersection of human and pet nutrition and lifestyle trends. As part of our annual report on U.S. supplement trends and consumer insights, we surveyed supplement consumers regarding their awareness, attitudes, and behaviors related to the category. This report presents several findings from this study, along with implications for supplement ingredient companies, manufacturers, and CPG brands.
Methodology
In March 2022, MarketPlace surveyed an online panel of 766 U.S. adults age 18 and older. Panelists, hereafter referred to as “supplement consumers,” were screened to include only respondents who reported consuming supplements daily, when they have a specific need, or infrequently within past six months. Certain data are compared to findings from MarketPlace’s 2020 human supplement study, which applied similar screening criteria to identify supplement consumers. Survey samples for both studies was provided by Dynata. Responses were tabulated and reported here in the aggregate, except where otherwise noted.
Key Findings
- Energy supplements continue to show promise, indicated by supplement consumers’ reported needs (low energy) and increased interest in energy as a functional benefit.
- Supplement consumers expressed interest in supplements for proactive and preventative measures, even more so than for management of an existing health state.
- While tablets, capsules, and gummies were the most preferred supplement formats for daily use, functional foods and beverages continue to capture the interest of supplement consumers.
- The spike in usage of vitamins and zinc parallels the rise in consumption of immunity supplements and indicates growth potential for immune health innovation.
- The data suggest a disconnect between actual and perceived consumption of medicinal mushrooms in supplements, indicating a need for education around these adaptogens.
- Supplement consumers are heavy information-seekers. A multi-channel approach to brand promotion that includes search engine marketing, media planning, and thought leadership creates numerous touchpoints for the audience to interact with and learn about a supplement brand.
- Consumers who have taken biomarker tests and those who use supplements to support their microbiome are more likely than the average supplement consumer to consider supplements made with adaptogens.
- Cultivating trust is essential to driving first-time purchases among supplement consumers. To encourage sharing among friends and family, marketers should consider a mix of word-of-mouth tactics and shareable social media assets. Positive reviews on online channels are also critical to converting this information-seeking audience.
Detailed Findings
Shifting Demand for Supplements by Need State
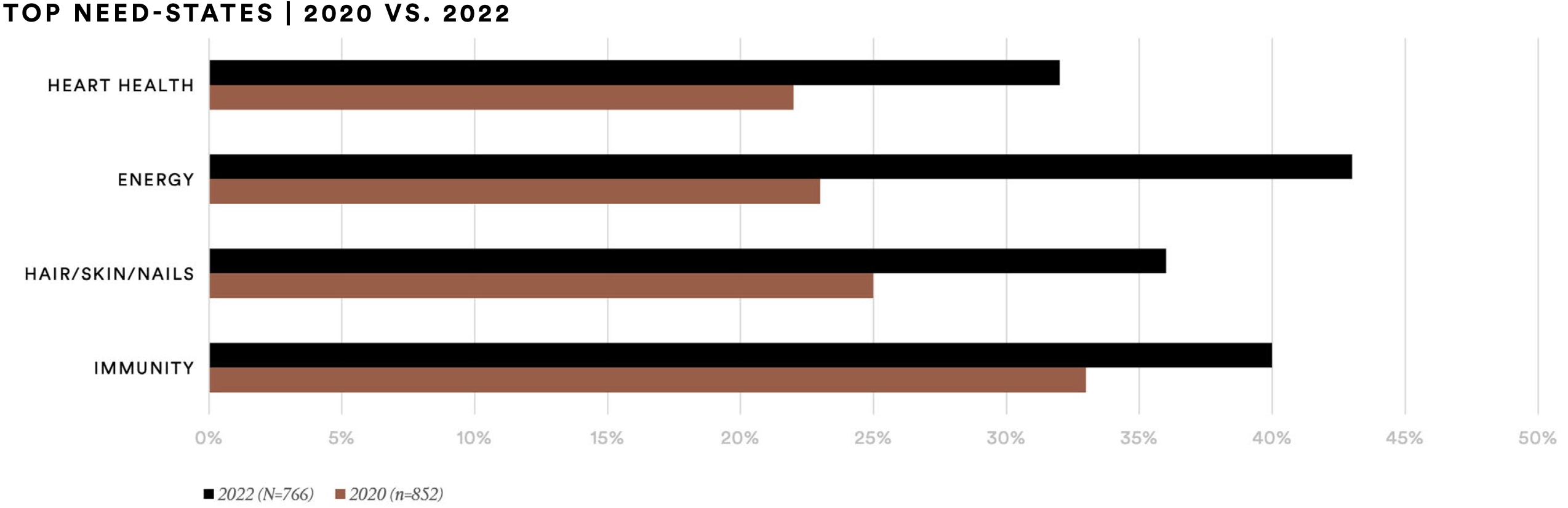
The need-states prioritized by U.S. supplement consumers shifted in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. In 2022, their demand for energy (43%), immunity (40%), hair, skin, and nail (36%), and heart health (32%) supplements increased substantially in comparison to 2020.
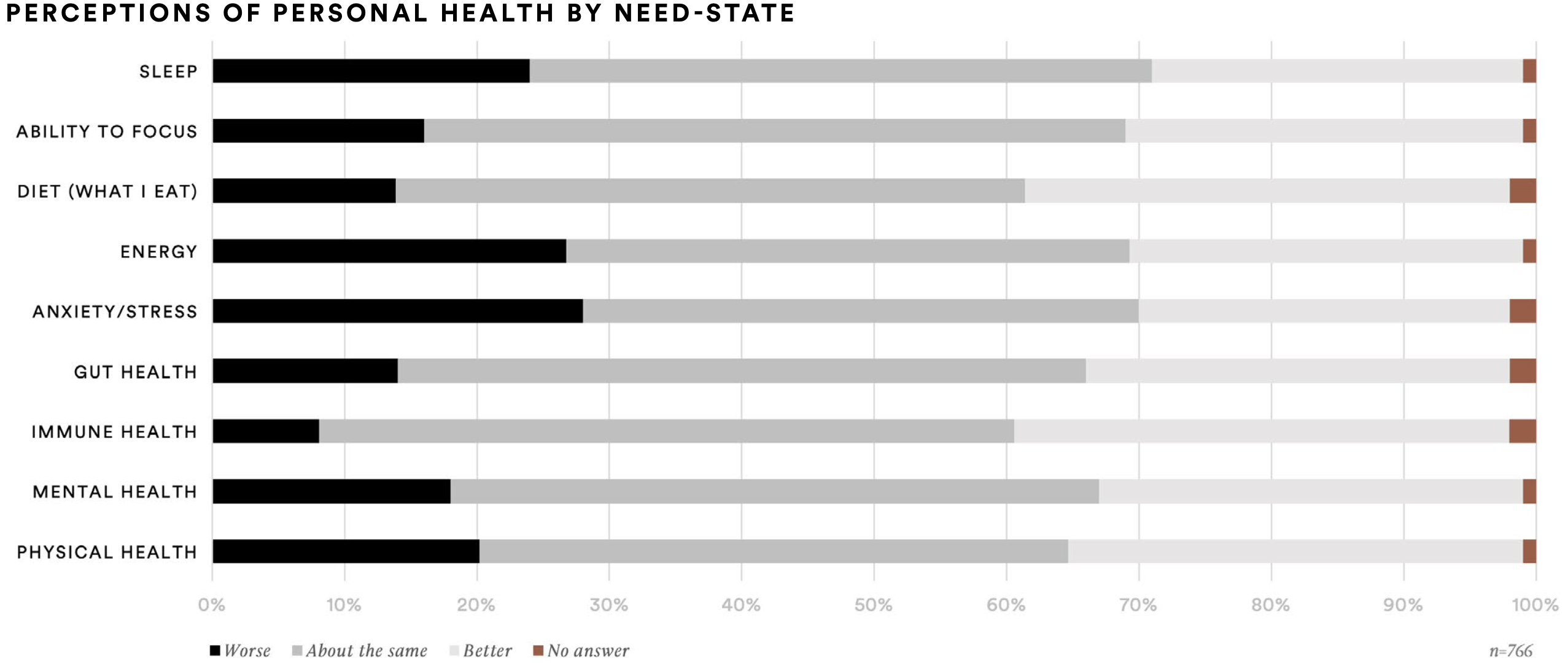
Perceptions of personal health also shifted in the past two years. When asked to describe aspects of their health compared to two years ago, more than one-third report their immune health (37%) or diet (37%) is better. Conversely, more than one-fourth report their anxiety/stress levels (28%) or energy (27%) are worse than compared to two years ago.
Reasons for Consuming Supplements
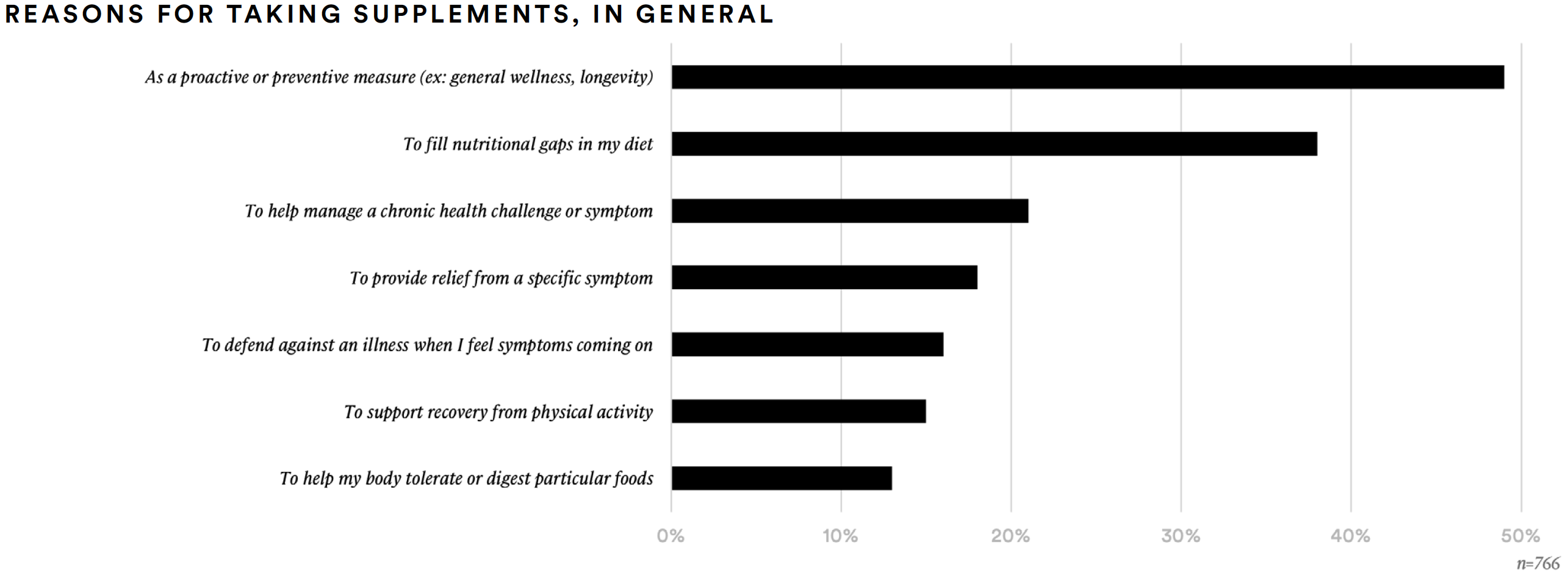
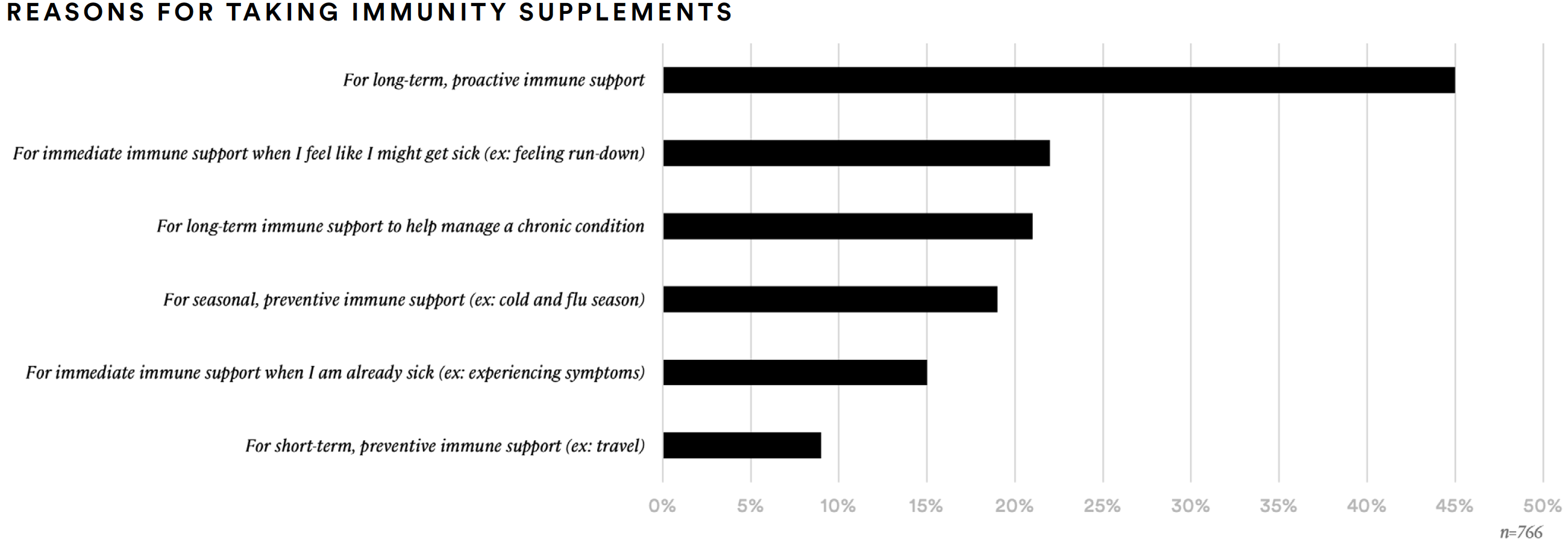
Nearly half of supplement consumers (49%) report taking supplements as a proactive or preventative measure. Similarly, 45% report taking immune health supplements for long-term, proactive immune support. More than one-third (38%) report taking supplements to fill nutritional gaps in their diets.
Over one-in-five (21%) take supplements to manage a chronic health challenge or symptom and approximately 22% take supplements for immediate immune support when they feel like they might be getting sick.
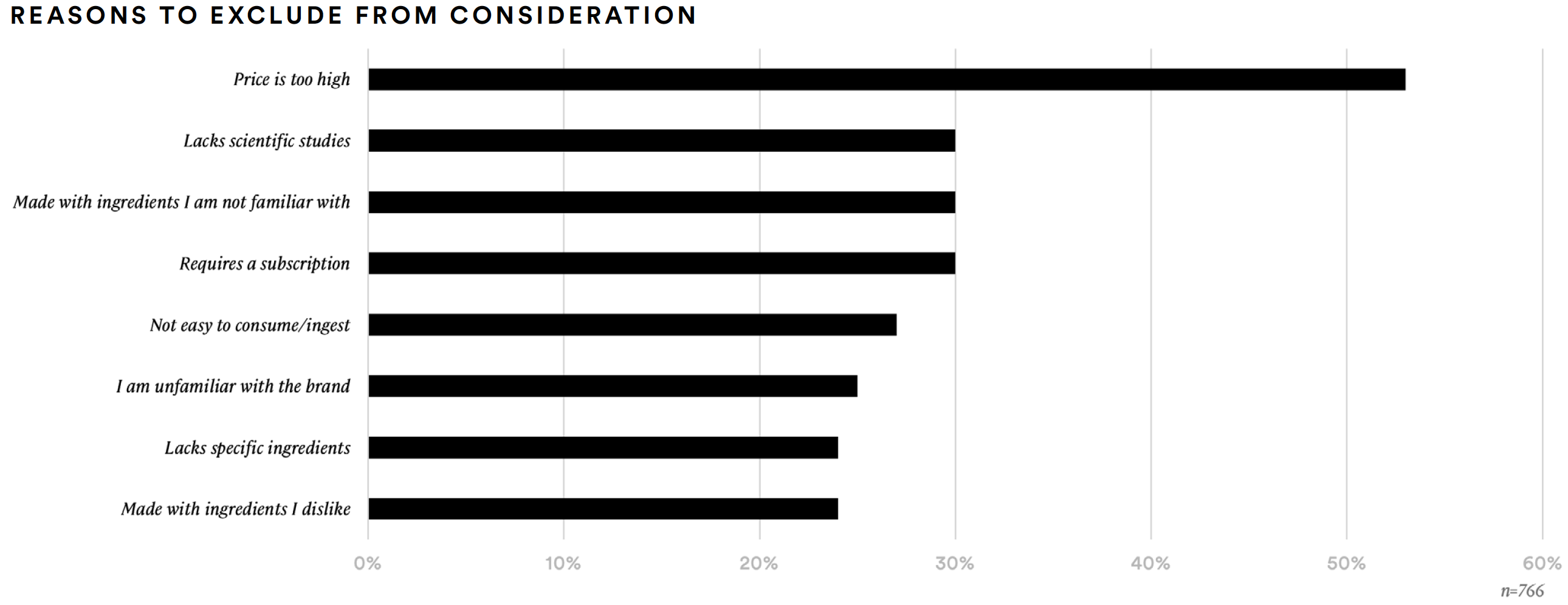
Price (53%), subscription requirement (30%), unfamiliar ingredients (30%), and lack of scientific studies (30%) are top reasons that consumers report might cause them to exclude a supplement from consideration.
Format Preferences
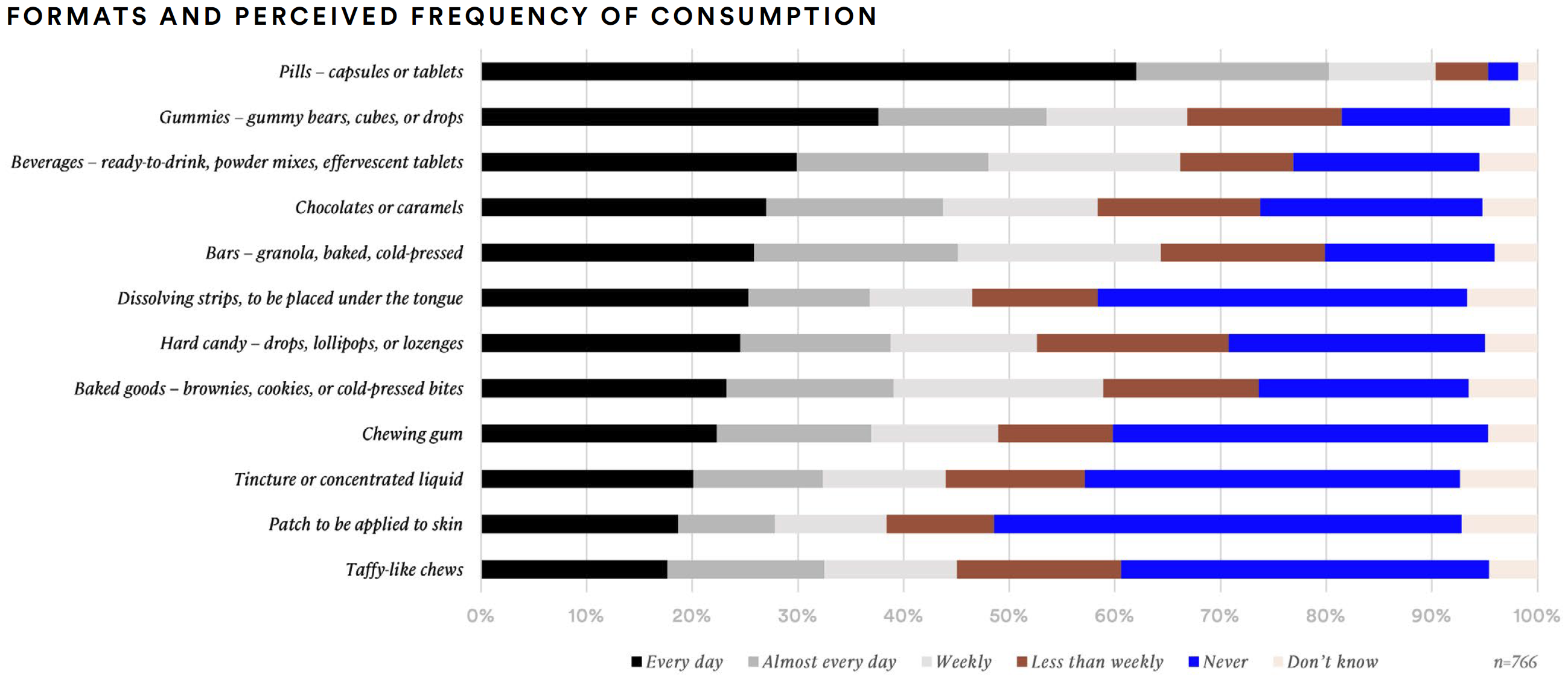
When it comes to formats that deliver the benefits or ingredients one might seek in supplements, a majority of supplement consumers (80%) said they would take pills (capsules or tablets) every day or almost every day. Gummies were the second most highly reported format for regular consumption (54%).
Including and beyond supplements, beverages hold appeal. Nearly half of supplement consumers reported that they would consume a functional beverage (48%) every day or almost every day if it contained the benefits or ingredients they would seek in supplements.
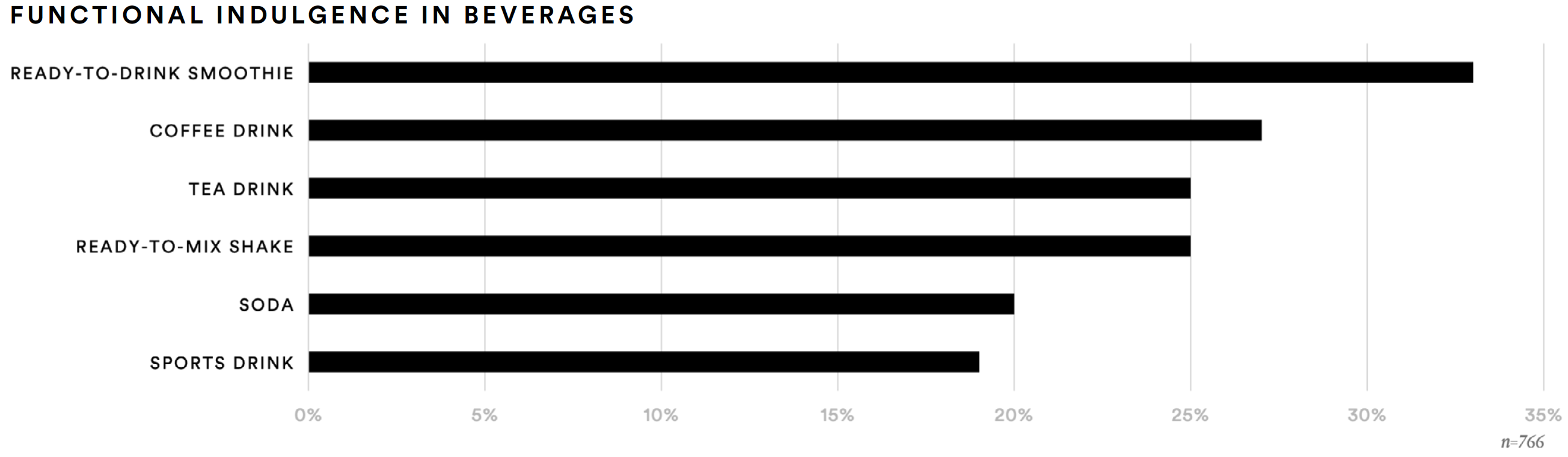
Supplement consumers also expressed interest in indulgent beverage formats to deliver the benefits or ingredients they would seek in supplements. About one-third (33%) said they would find ready-to-drink smoothies appealing. About one-in-four said the same for similarly beneficial coffee drinks (27%), ready-to-mix shakes (25%), or tea drinks (25%).
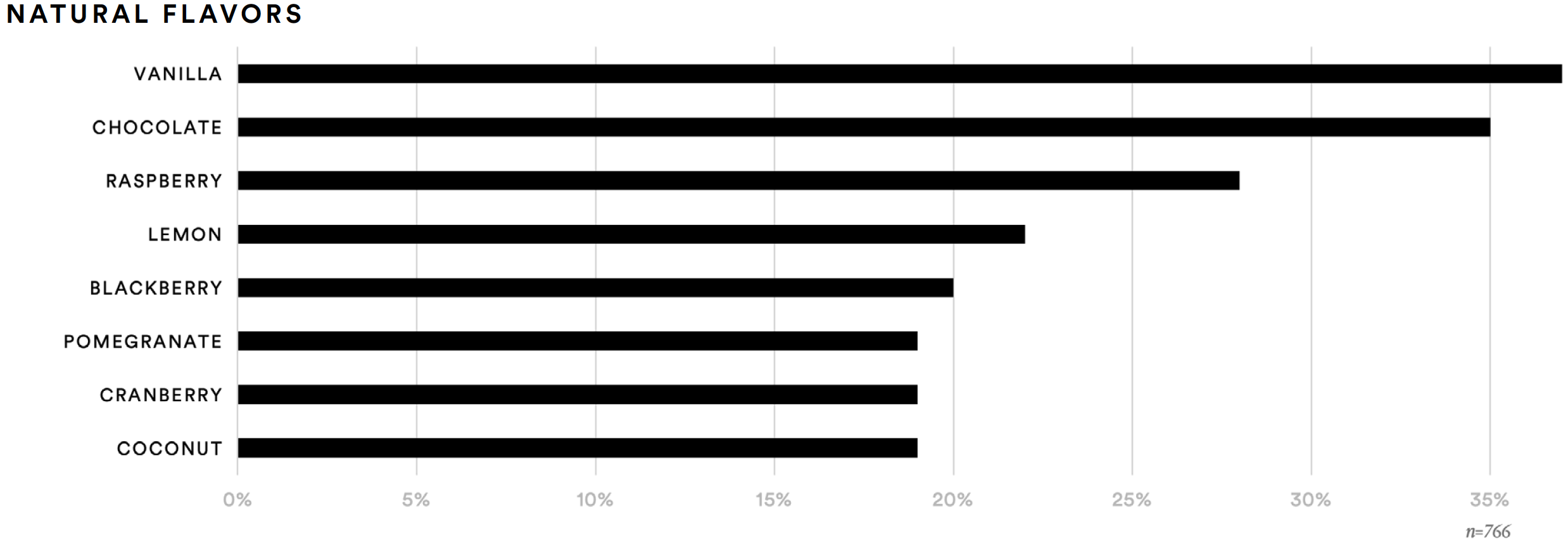
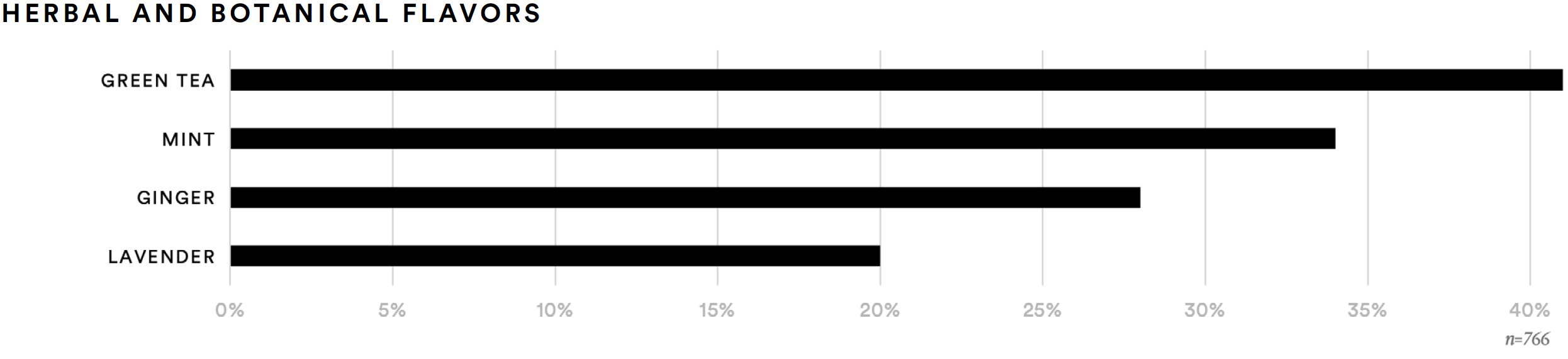
Respondents were presented with a list of natural flavors (e.g., vanilla, berries, citrus) and a list of botanical flavors (e.g., green tea, turmeric) and asked to identify up to three flavors from each list that they would find appealing in a better-for-you beverage. Among the natural flavors tested, supplement consumers were most likely to find vanilla (37%), chocolate (35%), and raspberry (28%) appealing. Among the leading botanical flavors were green tea (41%), mint (34%), and ginger (28%).
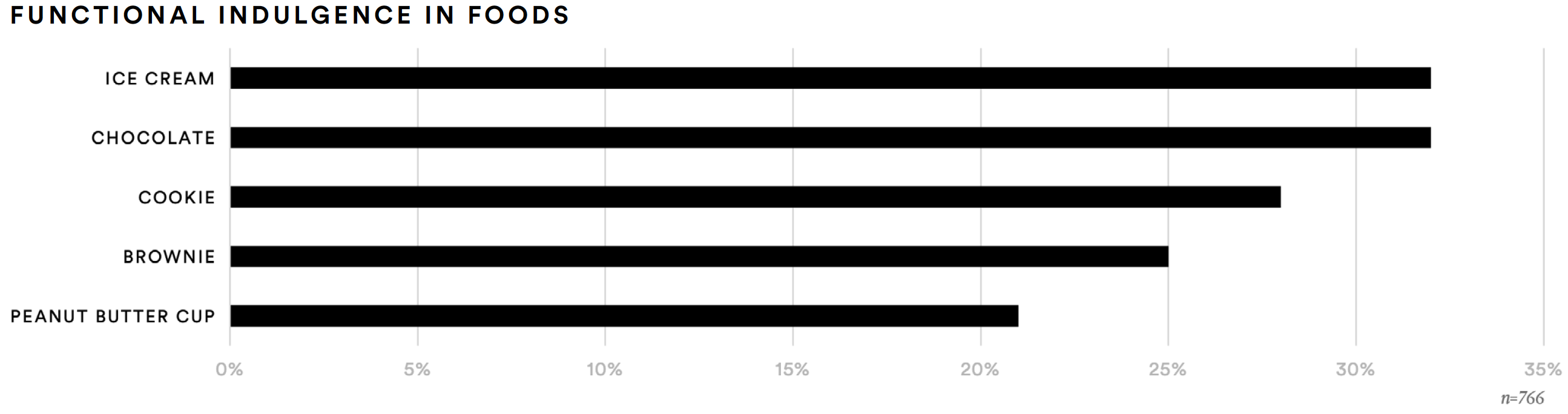
Supplement consumers also identified indulgent food formats they would find appealing if they offered the same health benefits they seek in supplements. Nearly one-third said chocolate (32%) or ice cream (32%) would have this type of appeal. About one-in-four said they would be interested in cookies (28%) or brownie (25%) that delivered these benefits.
Label Claims and Ingredients
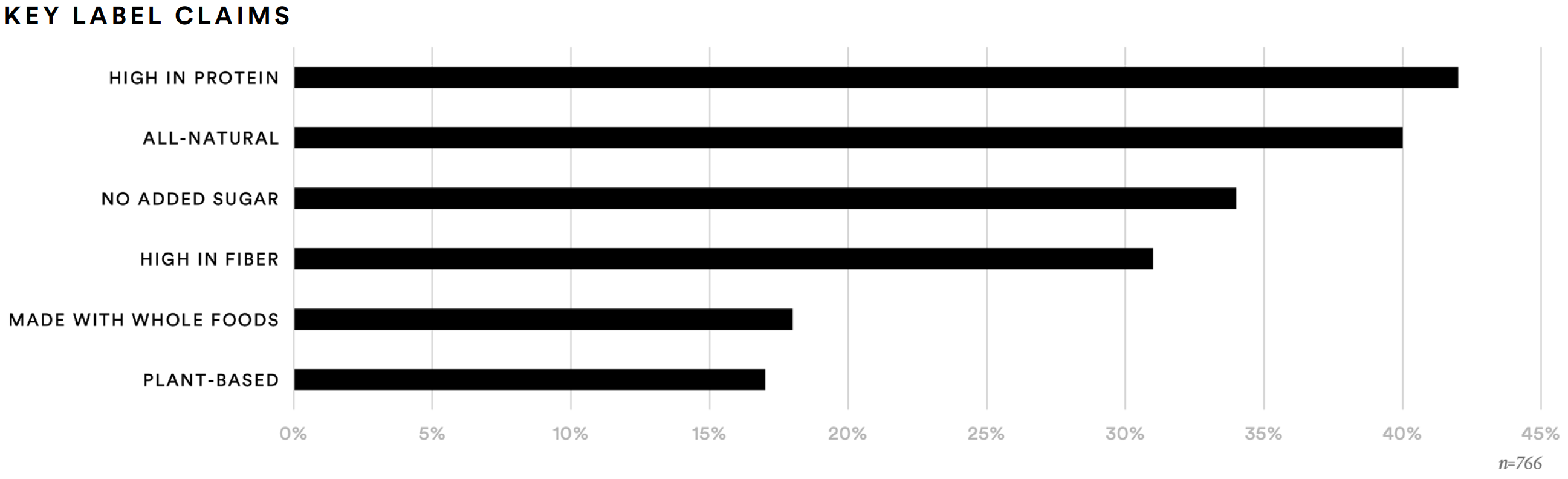
Certain label claims resonate strongly with supplement consumers. About two-out-of-five said they find “high in protein” (42%) and “all-natural” (40%) claims to be desirable, and about one-in-three said “no added sugar” (34%) or “high in fiber” (31%) are desirable.
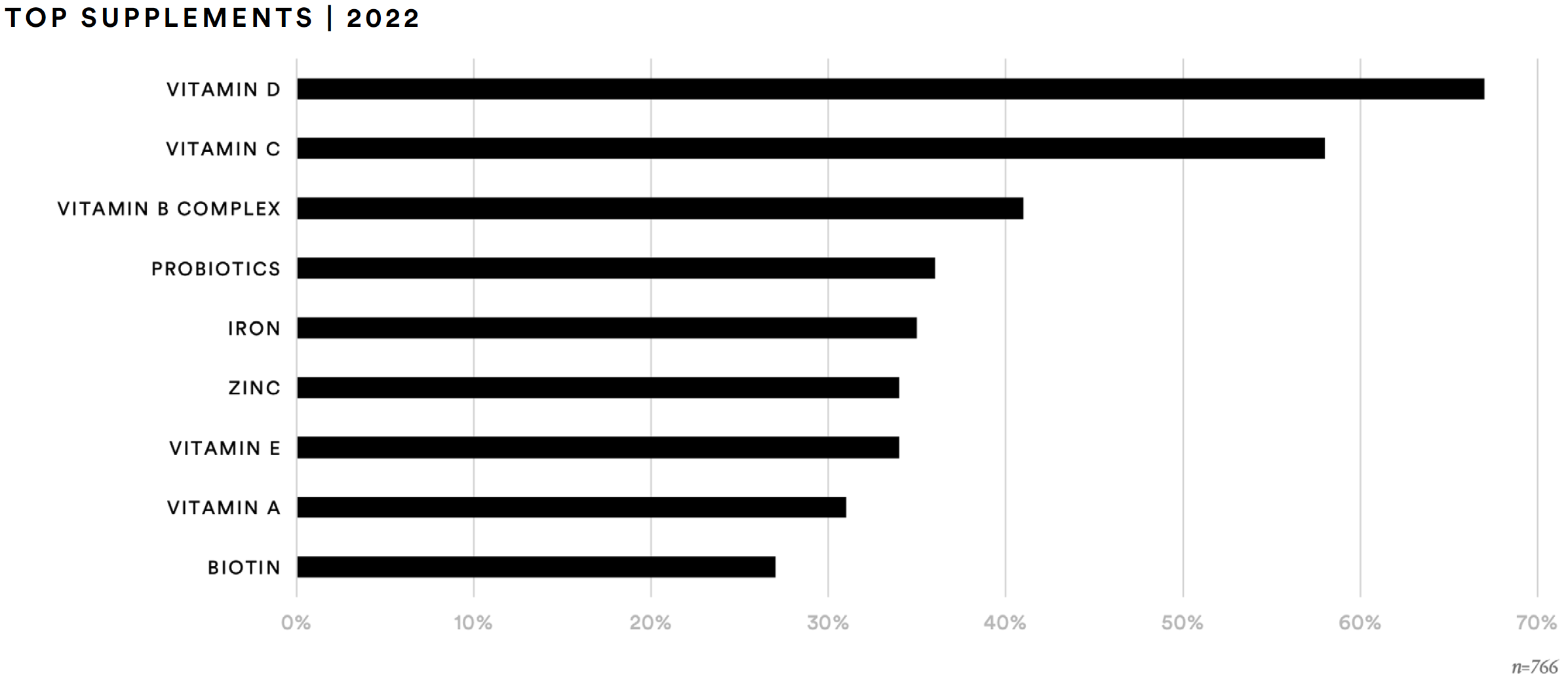
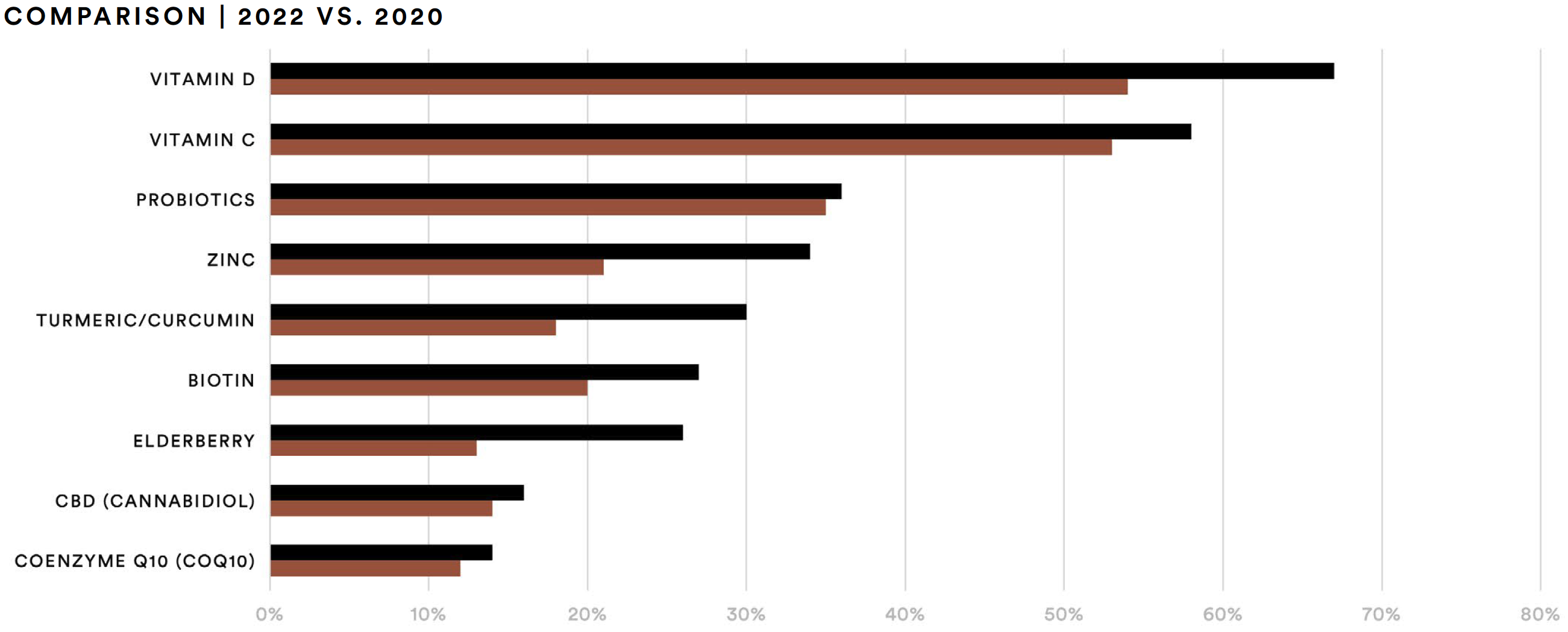
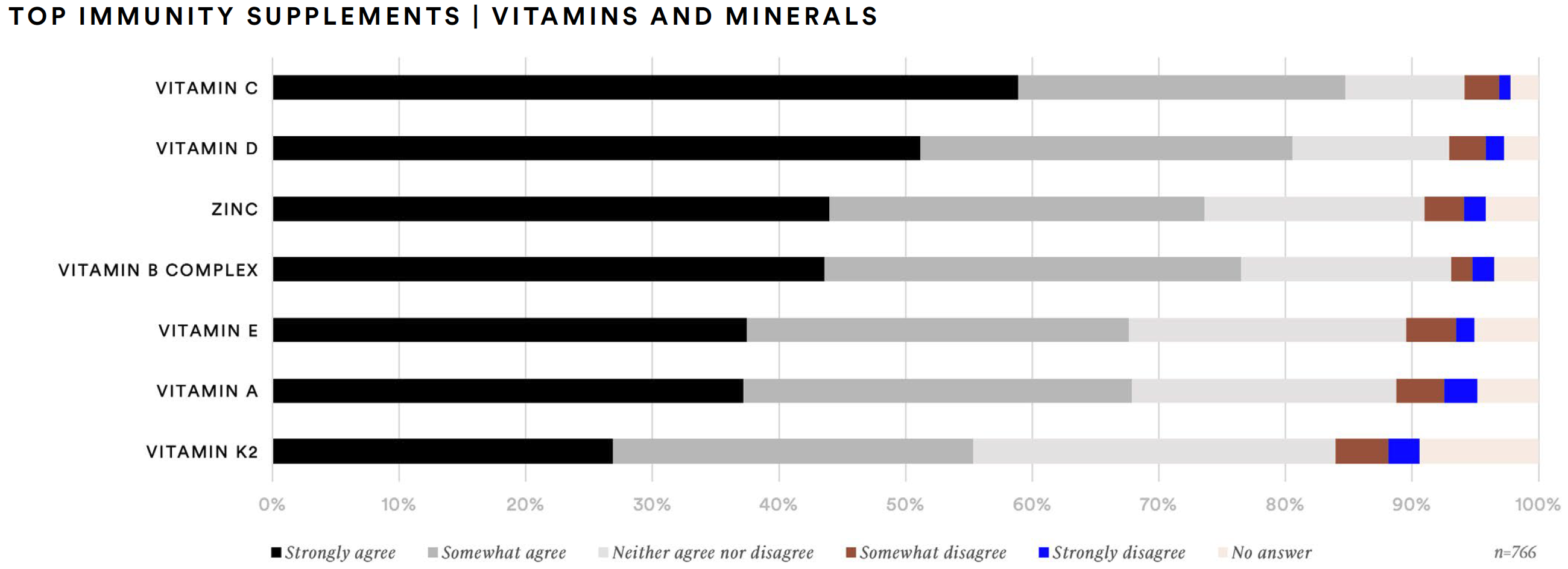
Likewise, certain ingredients are most sought-after by supplement consumers. Vitamins remain top-of-mind for this audience. Two-thirds (67%) of those surveyed said they have taken vitamin D in the past year. More than half (58%) report taking vitamin C and two-out-of-five said they have taken vitamin B complex. Compared to 2020, this represents a 13% increase for those who said they have taken vitamin D and a 5% increase for vitamin C.
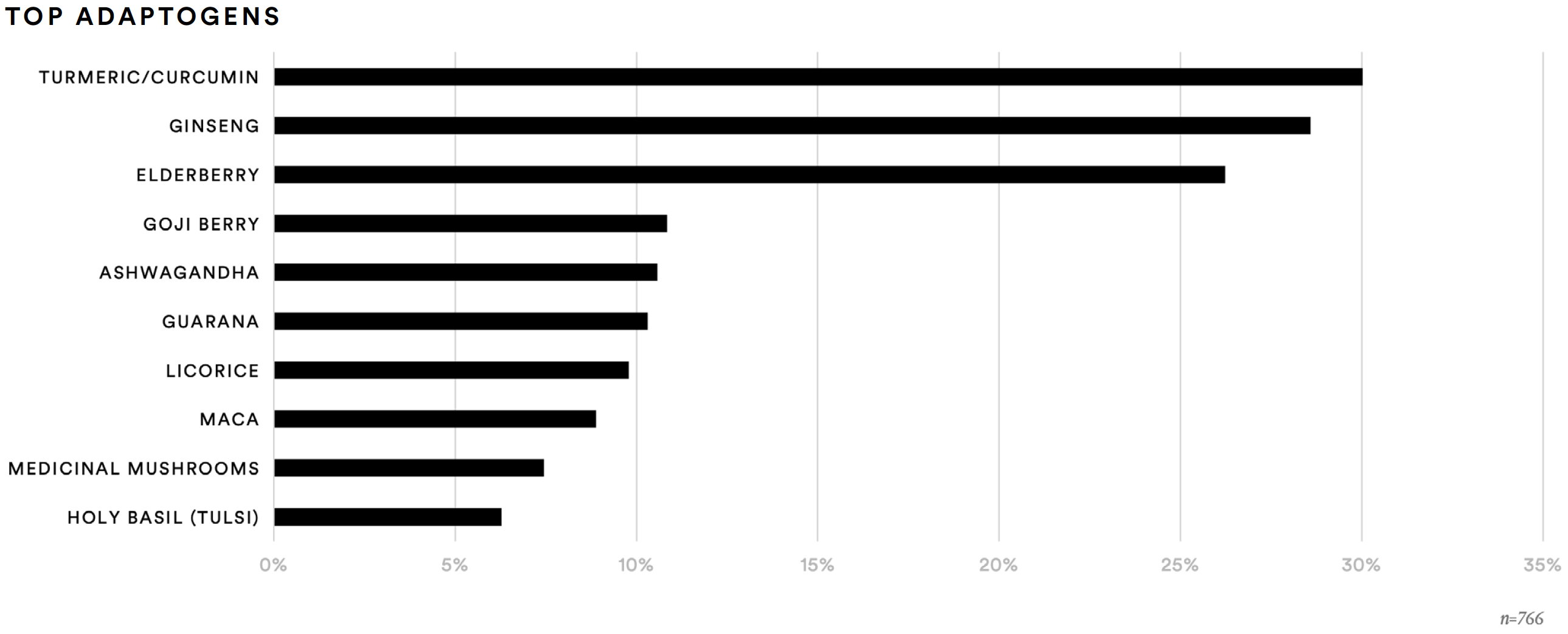
About one-in-three report taking vitamin E (34%) or vitamin A (31%) in the past 12 months. Similarly, about one-third of respondents reported taking probiotics (36%), iron (35%), or zinc (34%). While reported probiotics usage saw a modest increase of two percentage points compared to 2020, zinc usage increased by 13 percentage points. Slightly more than one-in-four (27%) report taking biotin in the past 12 months, about a 7% increase vs. 2020. The data also point to an increase in consumption of adaptogens, specifically turmeric and elderberry.
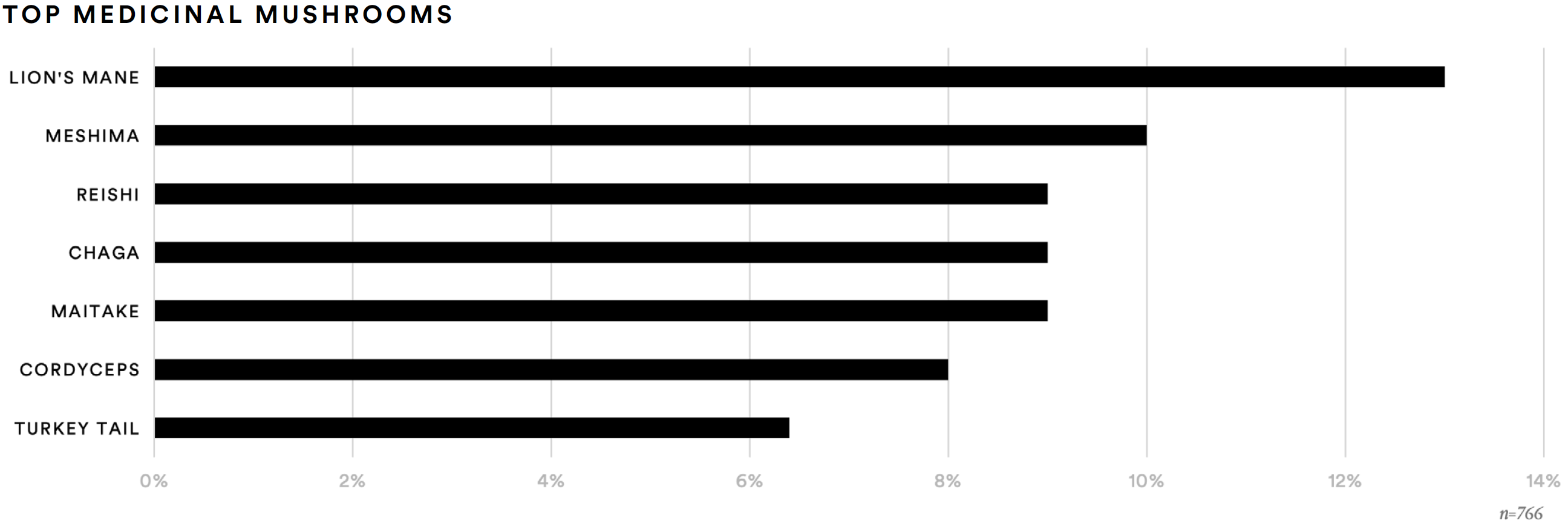
When asked if they’ve consumed “medicinal mushrooms” in the past 12 months, only 7% of respondents indicated that they had. However, when presented with a list of specific names of medicinal mushrooms, nearly 32% reported having taken at least one of the listed medicinal mushrooms in the past 12 months.
Among those who report consuming one or more specific medicinal mushrooms, more than two-out-of-five have taken lion’s mane (42%), and more than one-in-four have taken meshima (29%), chaga (28%), reishi (27%), or cordyceps (25%).
Immunity
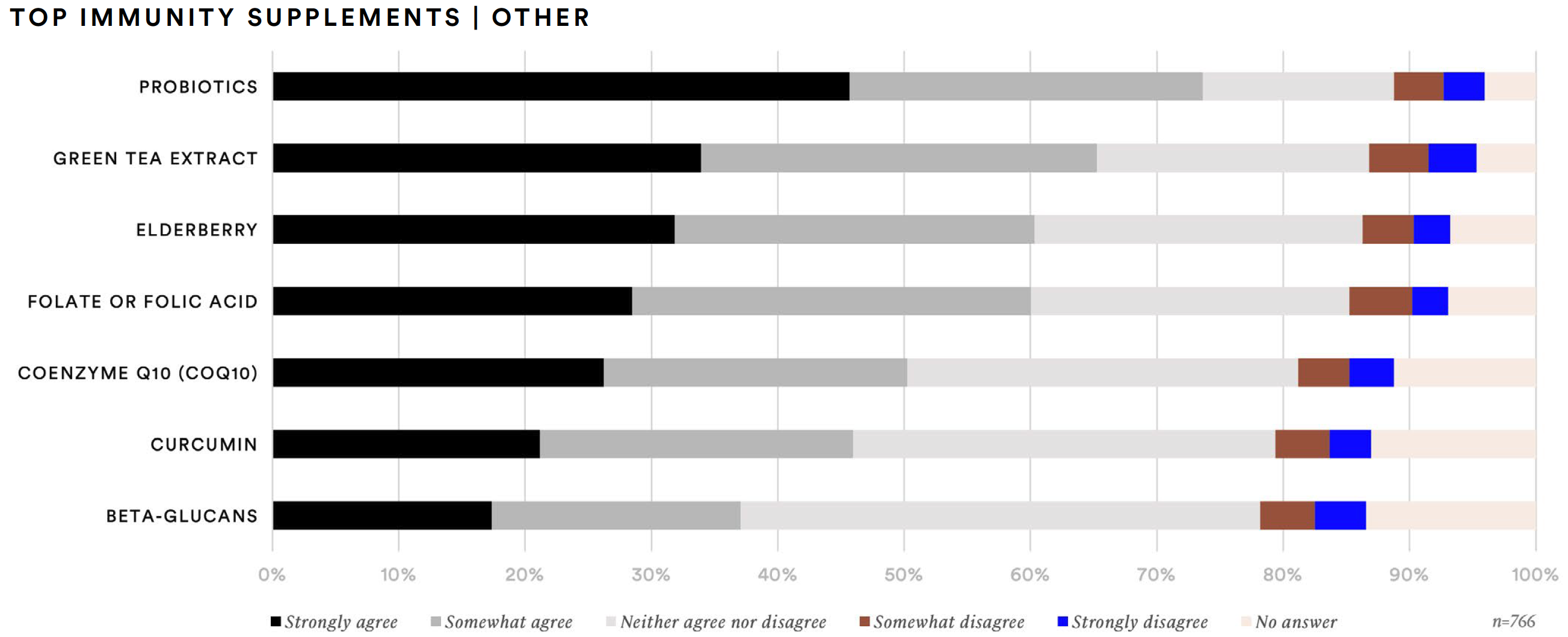
Vitamin C (85%), vitamin D (81%), vitamin B complex (77%), and zinc (74%) are the vitamin and mineral supplements consumers said they are likely to take to support immunity. Additionally, more than half of supplement consumers said they would take folate or folic acid (63%), green tea extract (63%), elderberry (57%), or probiotics (56%) to support immunity.
Researching Supplements
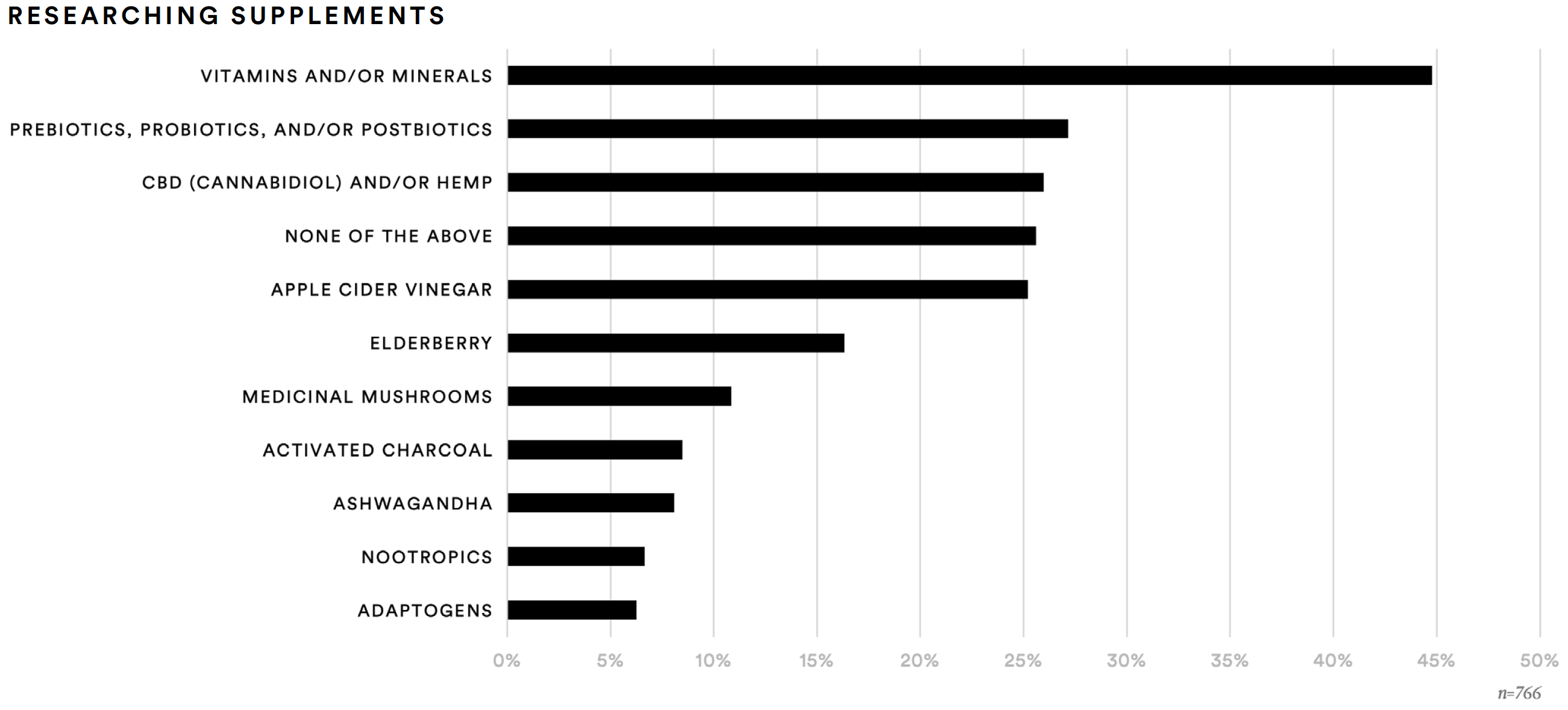
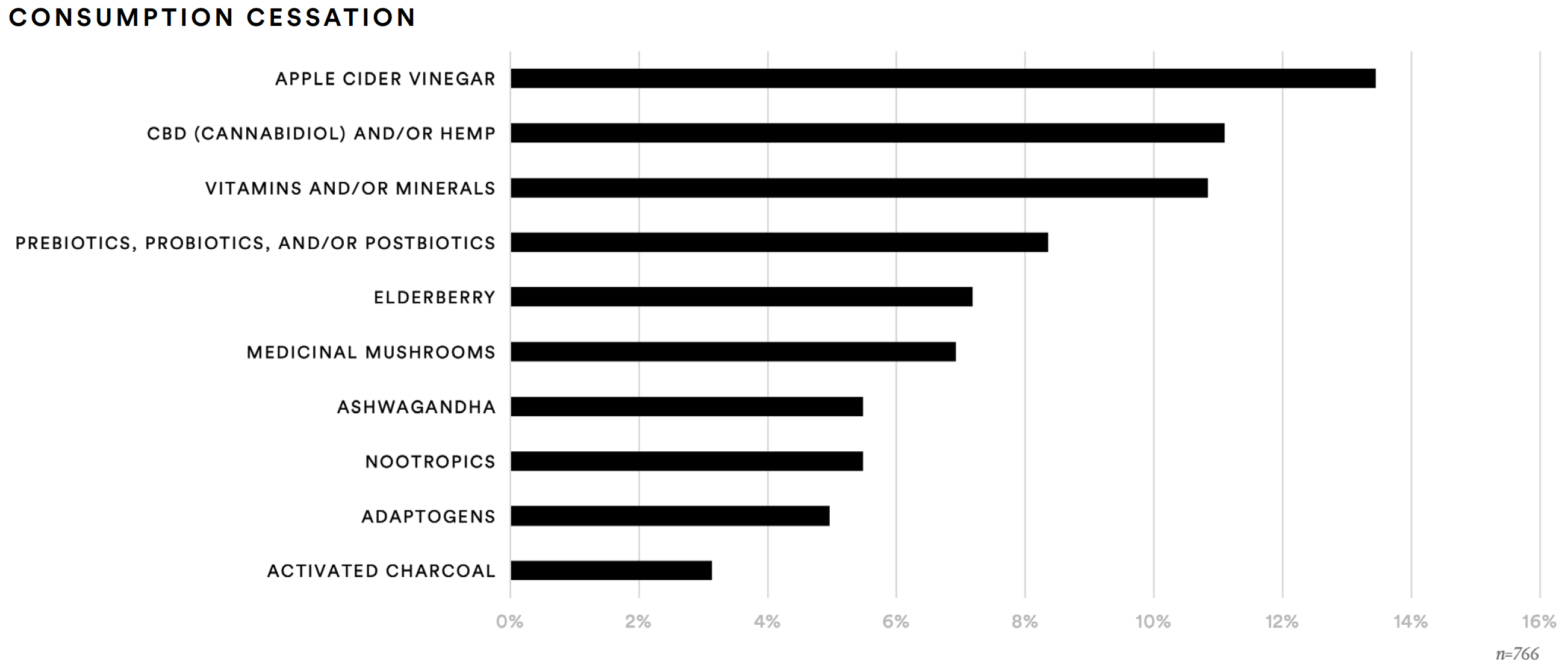
Researching supplements remains an important aspect of purchase decision-making for supplement consumers. A substantial number said that in the past 12 months they have spent more than an hour researching vitamins and/or minerals (45%), prebiotics, probiotics, and/or postbiotics (27%), CBD (cannabidiol) and/or hemp (26%), or apple cider vinegar (25%). Conversely, just over one-in-ten said they have stopped consuming apple cidr vinegar (13%), CBD and/or hemp (11%), or vitamins and/or minerals (11%).
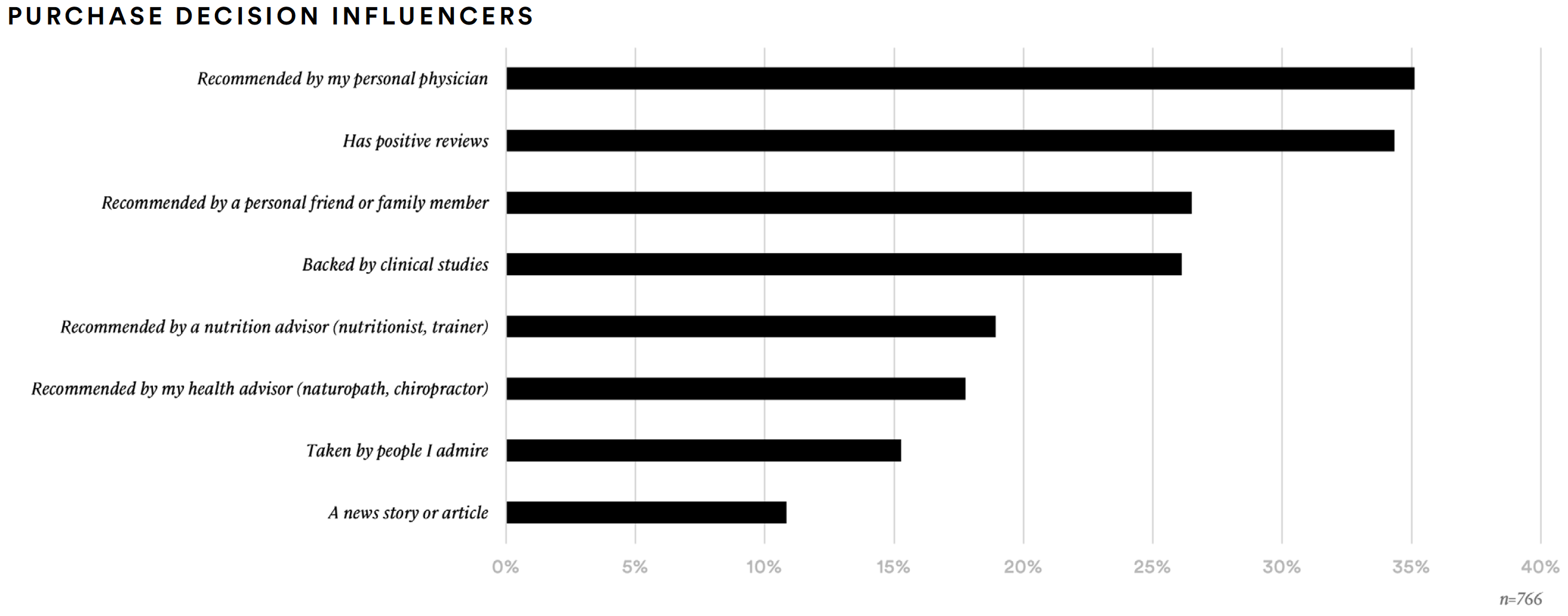
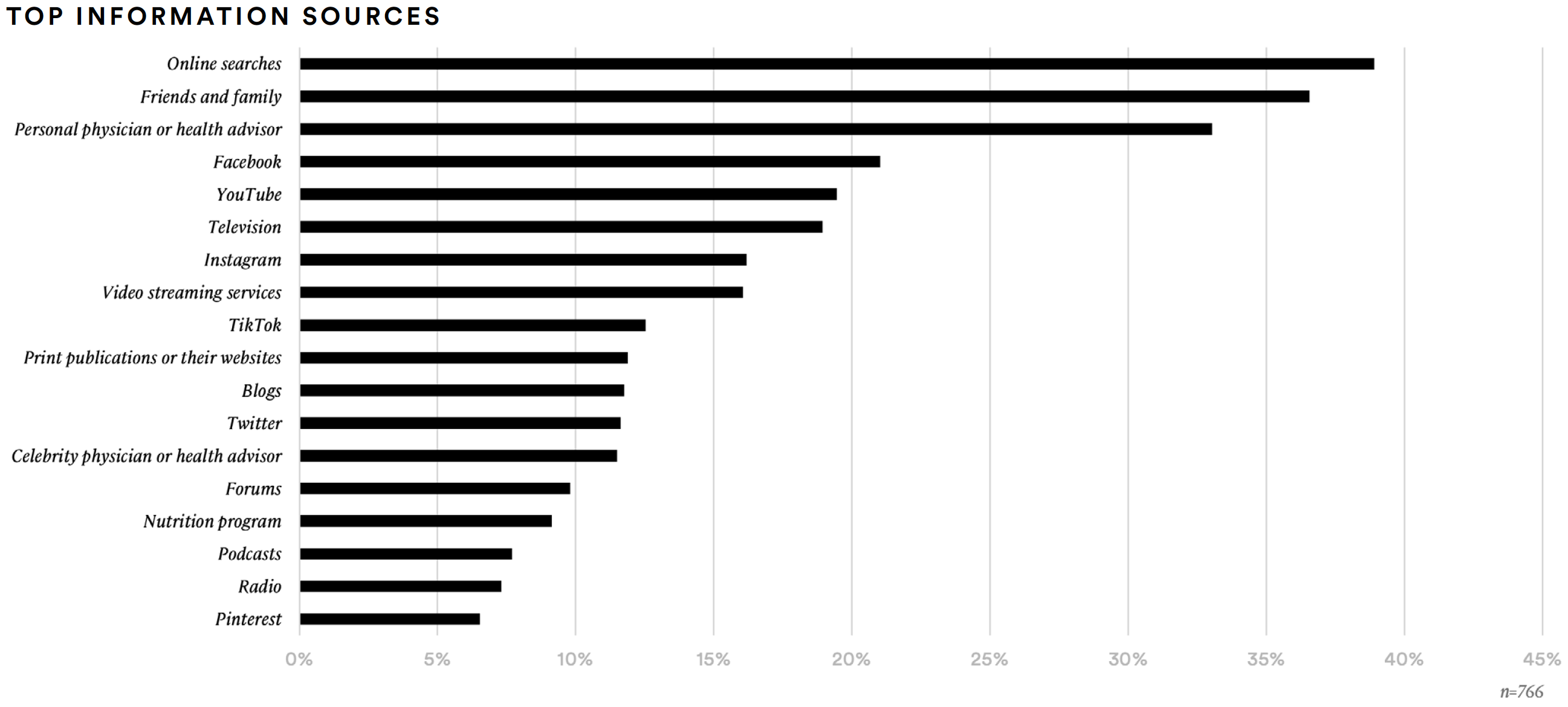
Supplement consumers were most likely to say that their attitudes about supplements are influenced by their personal physician (35%), positive reviews (34%), personal friends or family members (27%), or clinical studies (26%). Online search (39%), friends and family (37%), and personal physician (33%) are the top information sources for the audience.
Behavioral Categories
BIOMARKER
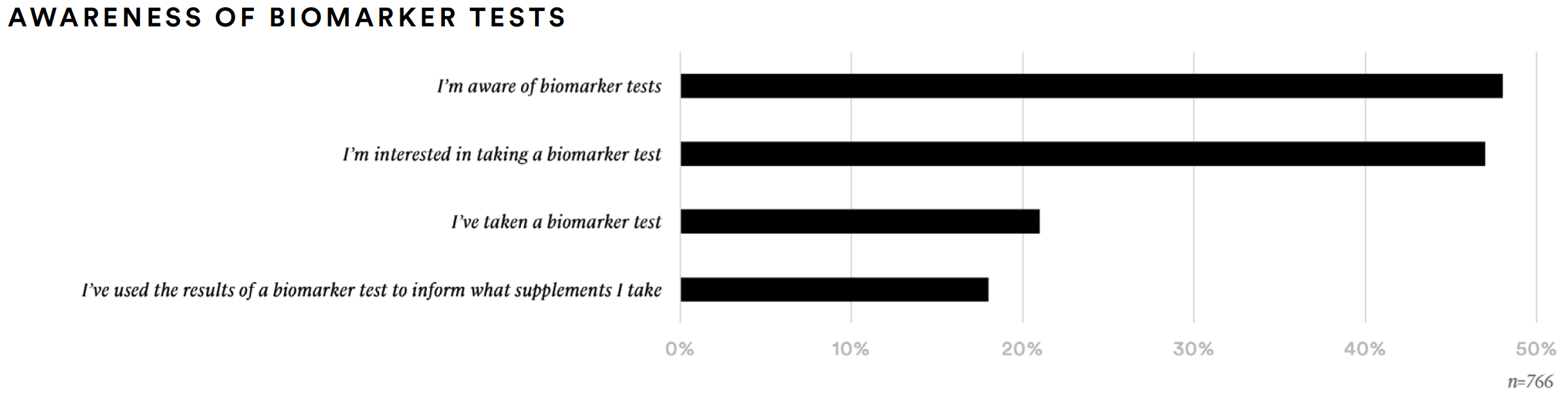
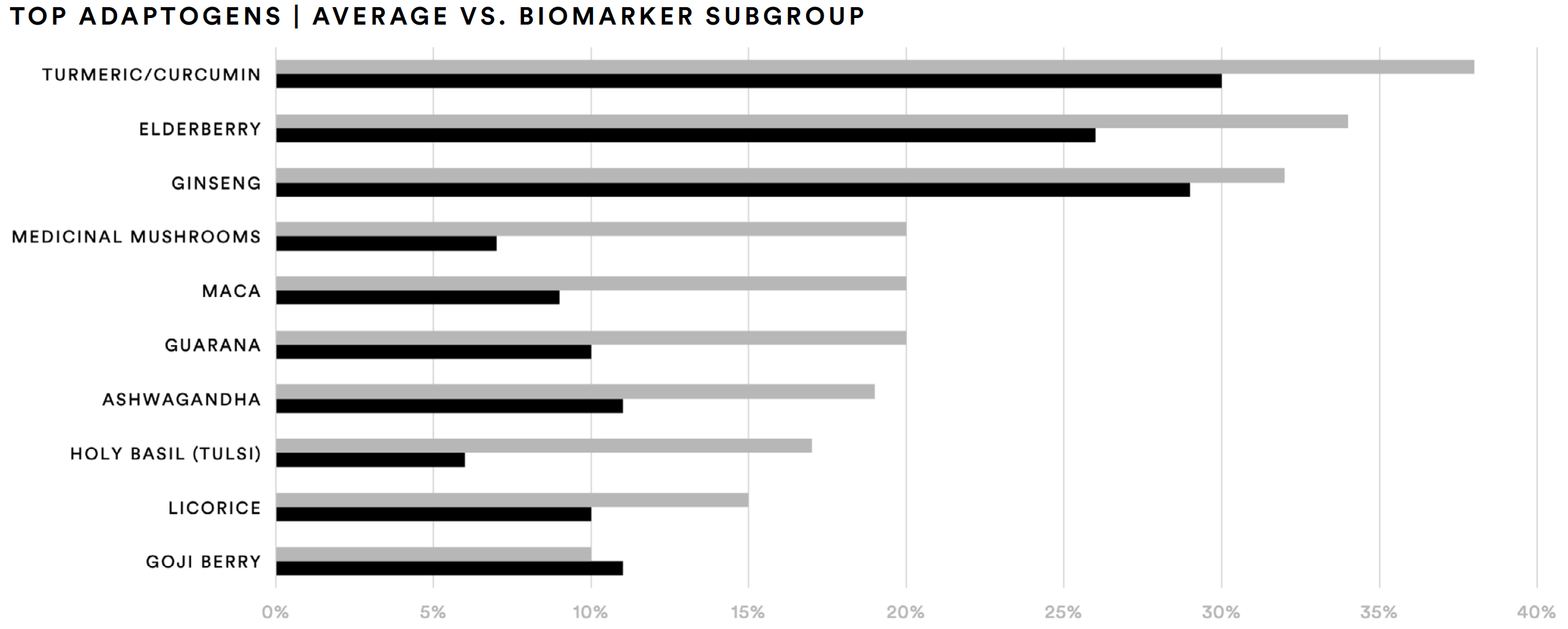
About one-half (48%) of supplement consumers said they are aware of biomarker tests and about one-in-five (21%) have taken them. Most of the supplements consumed by those who have taken a biomarker test (n=157) generally tracks with the average. However, the biomarker group was more likely to have taken adaptogens, such as turmeric/curcumin (38%), elderberry (34%), and ginseng (32%). This group was much more likely than the average supplement consumer to report having taken maca (20%), medicinal mushrooms (20%), guarana (20%), ashwagandha (19%), or holy basil (17%).
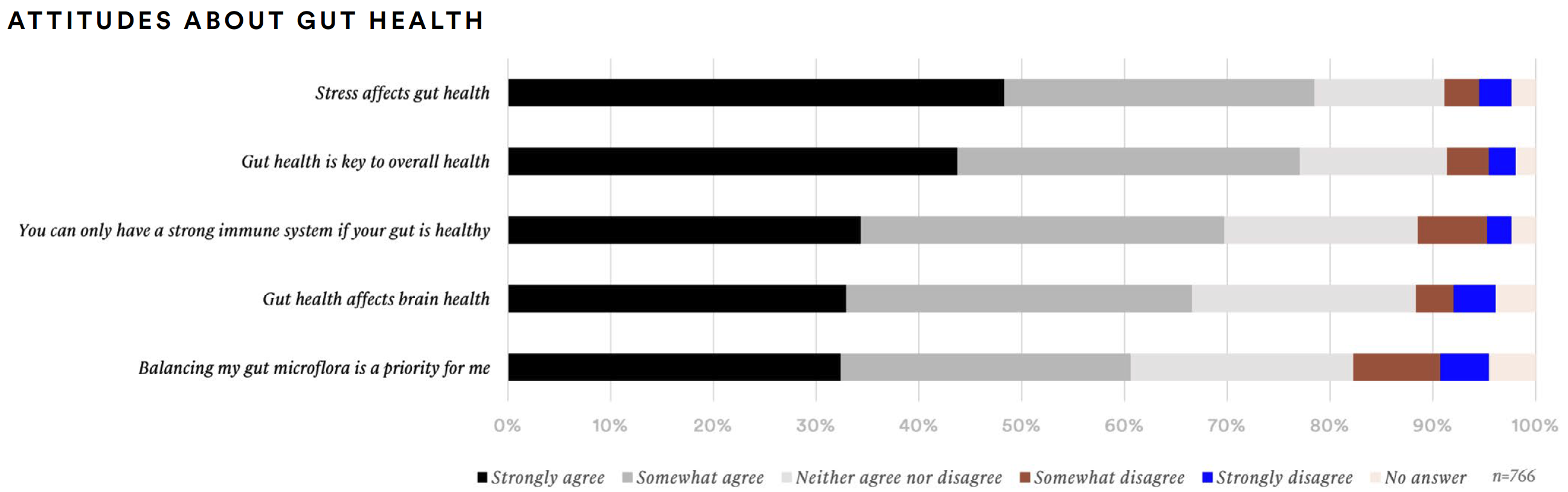
GUT HEALTH AND MICROBIOME
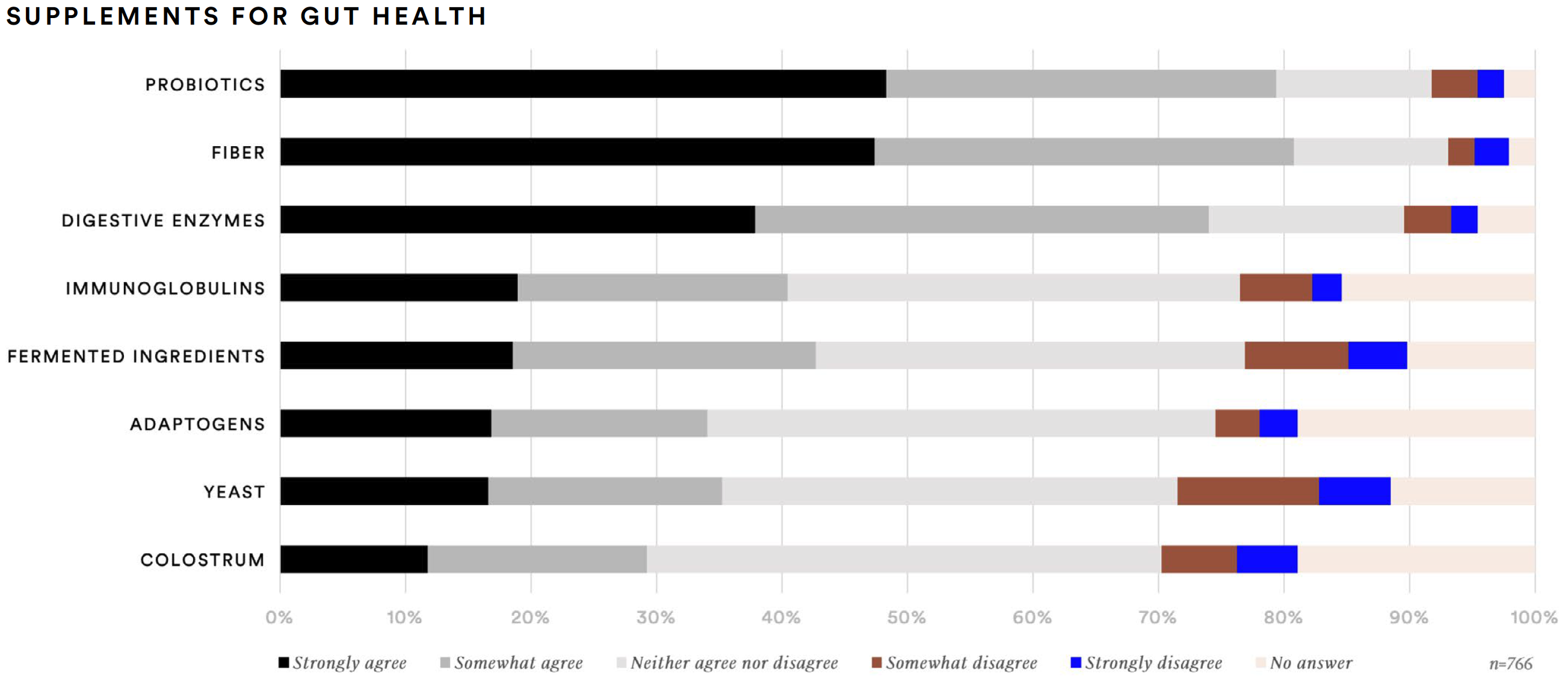
Overall, about three-out-of-four supplement consumers agree that stress affects gut health (78%) or that gut health is key to overall health (77%). About two-thirds (67%) agree that gut health affects brain health. Balancing gut microflora is a priority for three-out-of-five (61%). Fiber (81%), probiotics (79%), and digestive enzymes (74%) are the supplements consumers said they are likely to take to improve gut health.
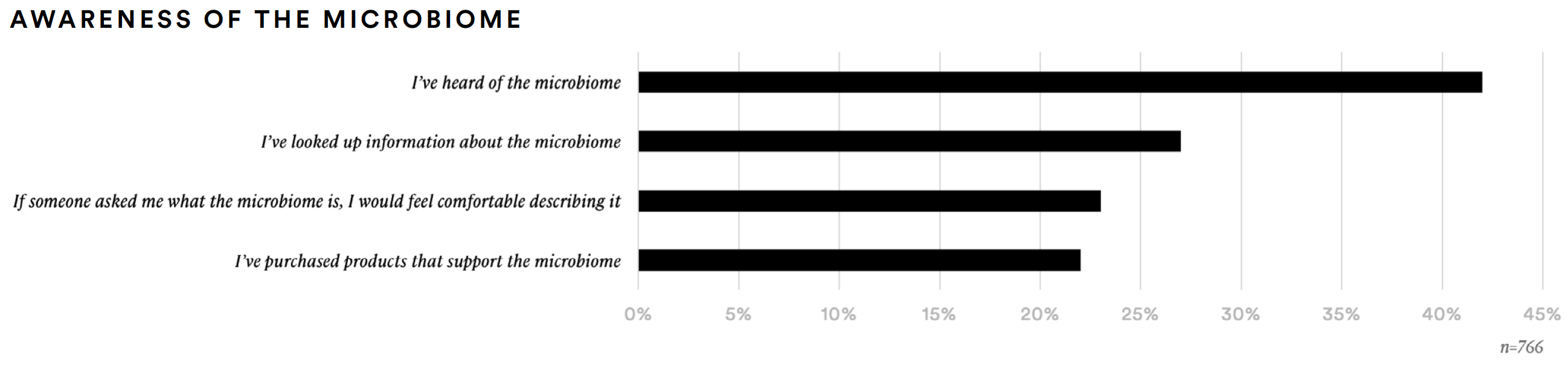
About 42% of supplement consumers said they are aware of the microbiome and about one-in-five (22% have taken products to support the microbiome. Respondents from this subgroup (n=168) are more likely than average to say they have taken probiotics (40%) and digestive enzymes (20%). They are much more likely than average to report taking prebiotics (21%).
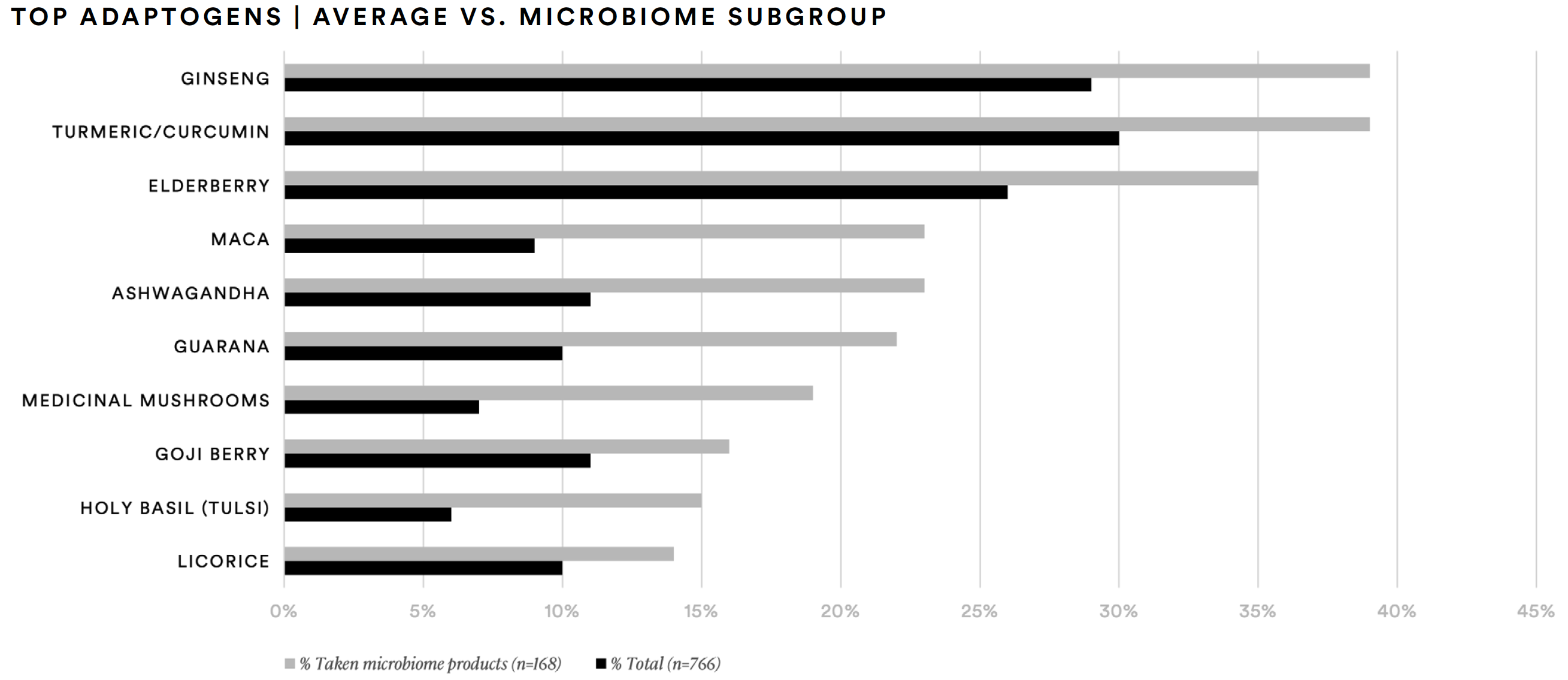
Like the biomarker subgroup, the microbiome subgroup was more likely to have taken adaptogens, such as turmeric/curcumin (39%), elderberry (35%), and goji berry (16%). This group was much more likely than the average supplement consumer to report having taken ginseng (39%), maca (23%), medicinal mushrooms (19%), guarana (22%), ashwagandha (23%), holy basil (15%), or licorice (14%).
Psychographic Motivators
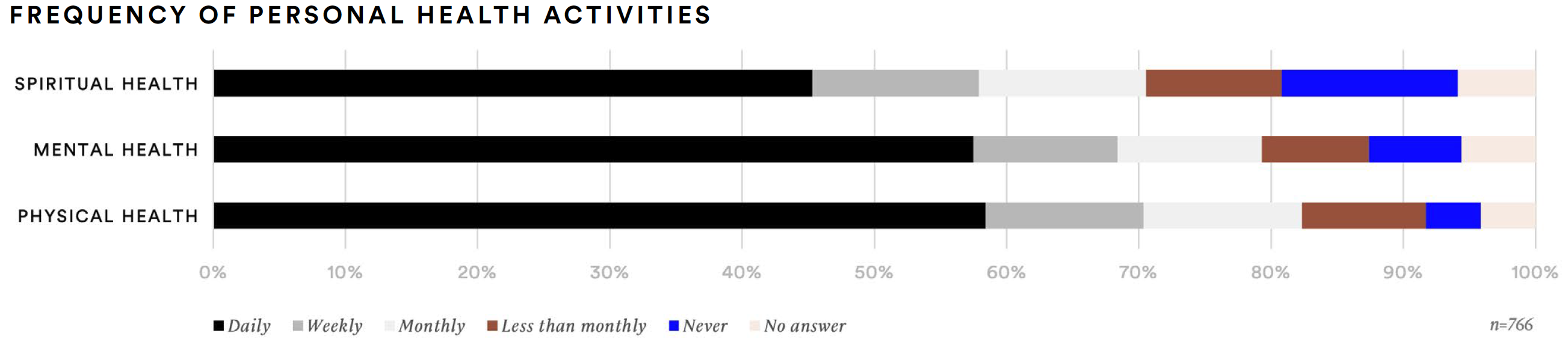
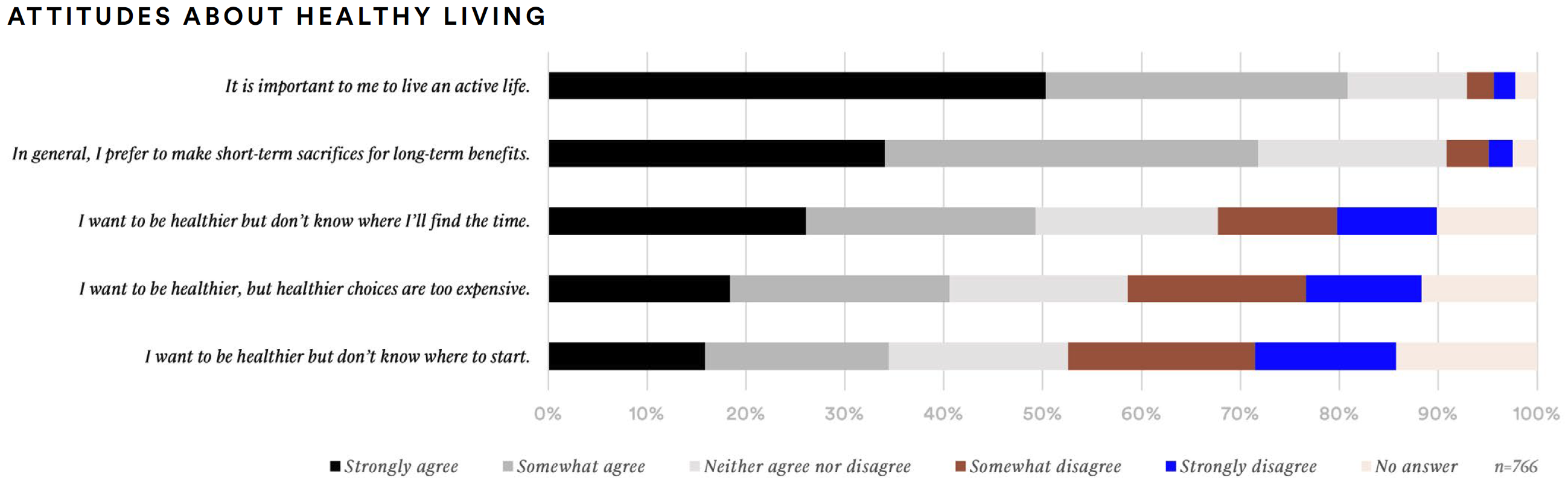
More than half of supplement consumers report participating in activities at least once per week to benefit their physical health (53%), mental health (57%), or spiritual health (51%). More than four-out-of-five (81%) agree that it is important to live an active life; over half (51%) strongly agreed with this statement. Seven-out-of-ten supplement consumers also agreed they prefer to make short-term sacrifices for long-term benefits. Moreover, 54% want to be healthier but feel choices are too expensive. Similarly, many supplement consumers want to be healthier but don’t know where to start (45%) or don’t know where they will find the time (39%).
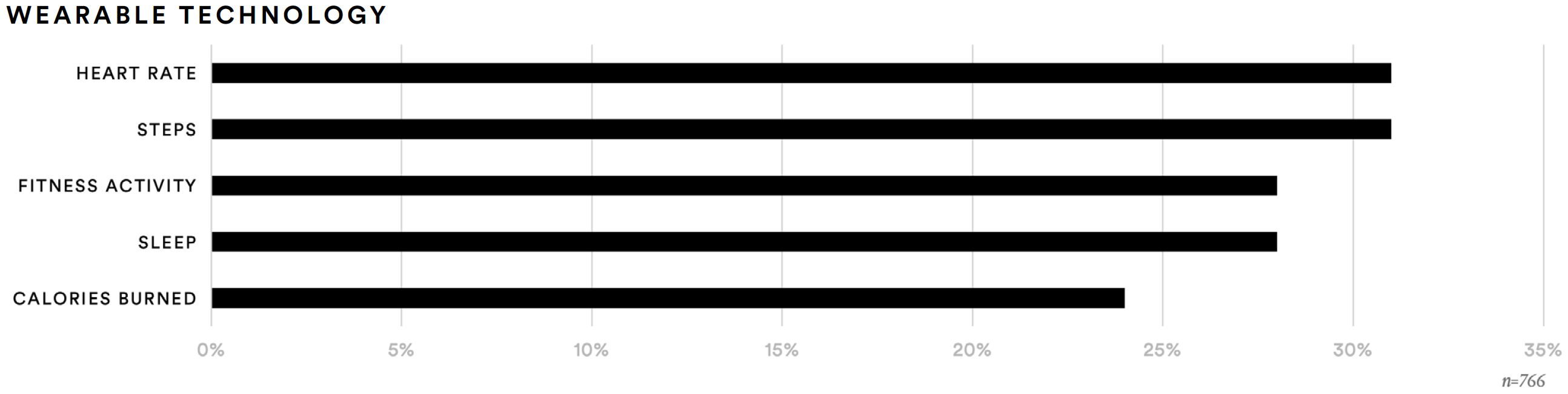
About 31% of supplement consumers said they use wearable technology to monitor their steps or heart rate. Another 28% said they also use these devices to monitor sleep and fitness activity. Furthermore, 24% report using wearable technology to monitor calories burned.
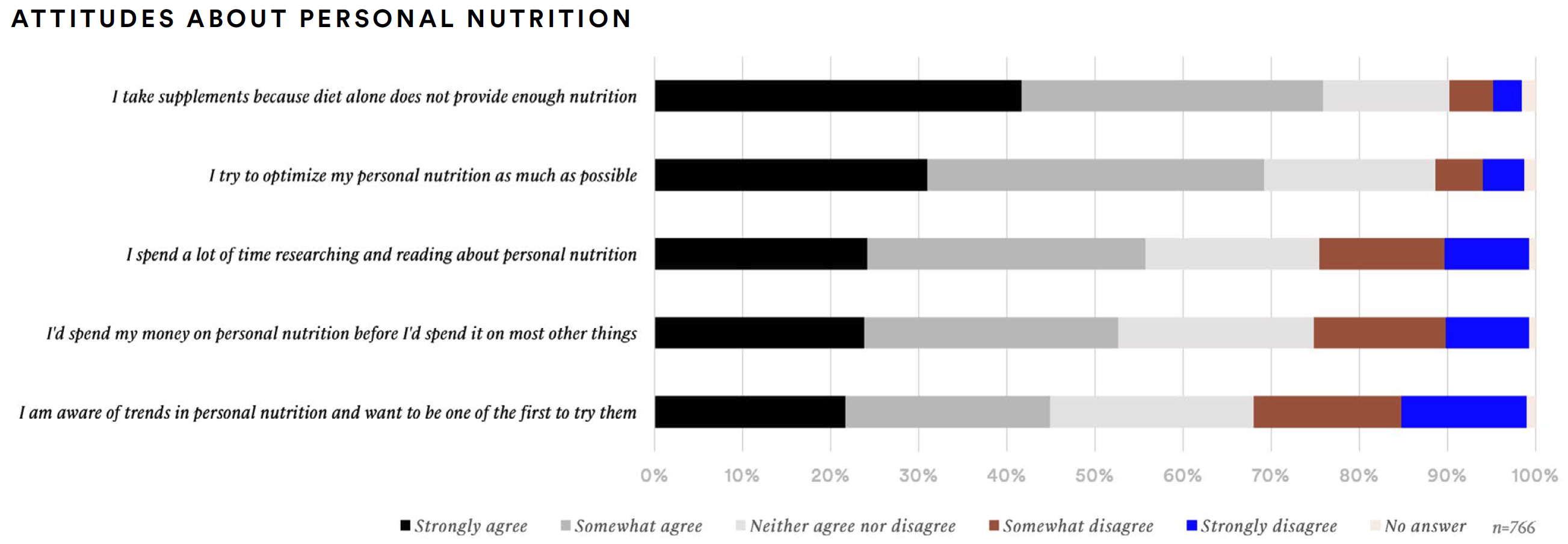
Personal nutrition is a top priority for supplement consumers. Nearly seven-in-ten (69%) agreed that they try to optimize their personal nutrition and 76% agreed that they take supplements because diet alone does not provide enough nutrition. More than half agreed that they spend a lot of time researching and reading about personal nutrition (56%) or that they spend money on personal nutrition before other things (53%).
First-Time Purchase Factors
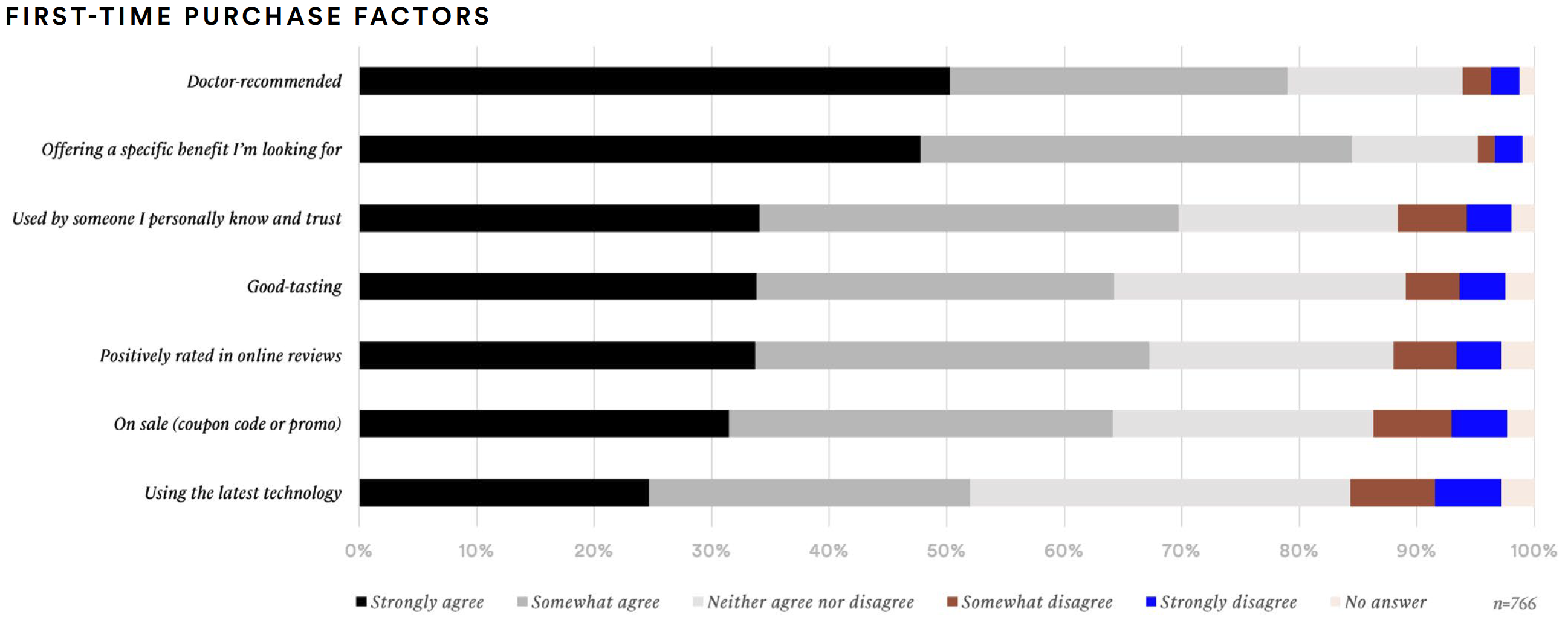
Overall, when shopping for supplements, supplement consumers are most likely to look for a specific benefit. It should be noted that their purchase intention is also highly influenced by trusted information sources like a doctor (79%), a trusted person they know (70%), and positive reviews (67%).
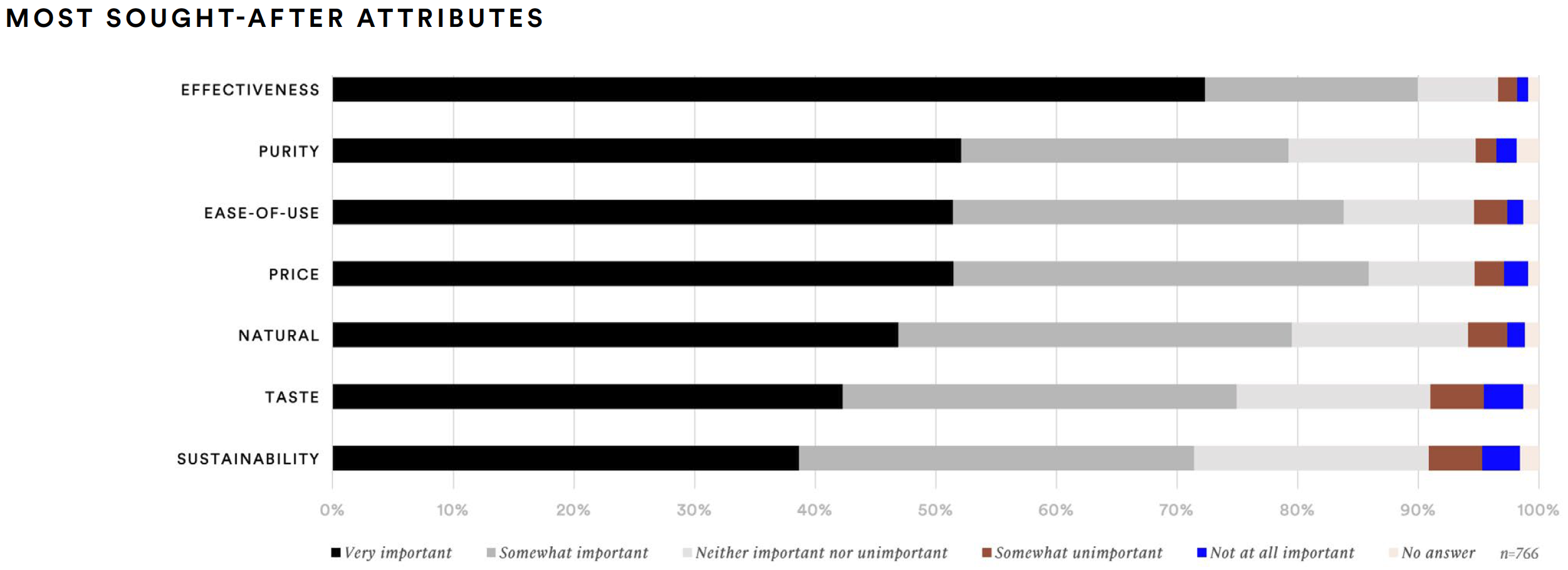
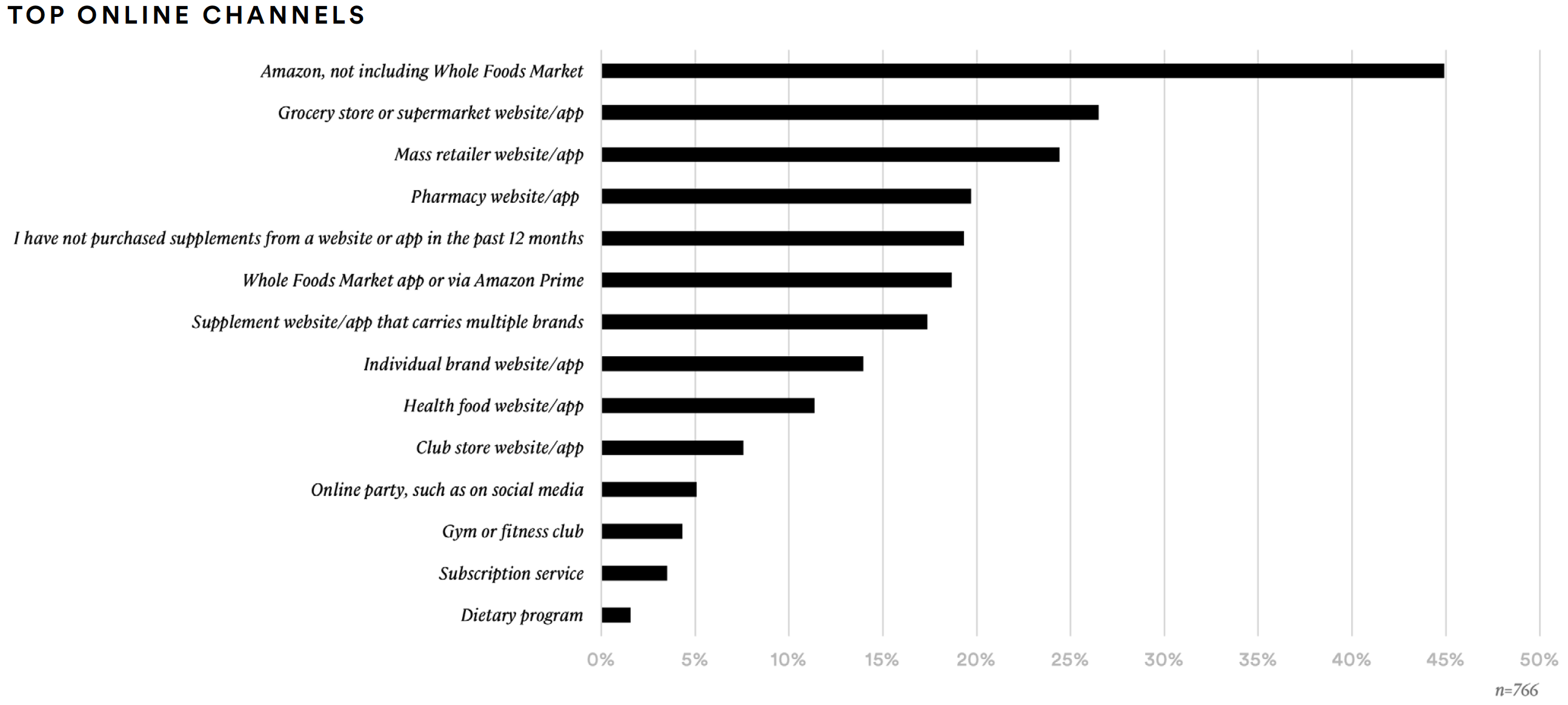
Furthermore, in supplements they are most likely to try for the first time, supplement consumers are most interested in effectiveness, price, ease-of-use, naturalness, and purity. Moreover, the online channels from which they are most likely to purchase supplements are Amazon (45%), grocery store or supermarket websites and apps (27%), mass retailer websites and apps (24%), and pharmacy websites and apps (20%).
There is Always More to Know
If you have an editorial request or would like to request more information about our study, please contact
us at hello@marketplacebranding.com.
Working With MarketPlace
Founded in 2002, MarketPlace is a strategic partner to health and wellness, pet and animal, and food and beverage brands. Through business strategy, industry focus, and marketing expertise, we help our partners grow.
If you’re working to launch a supplement or functional food and beverage brand, we do that, too—let’s talk!